Report
Citizen Lab research partner, Open Effect, announced the release of the full report detailing our year-long research collaboration into the privacy and security of wearable fitness tracking devices.
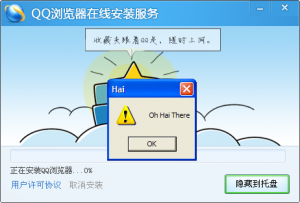
This report describes privacy and security issues with the Windows and Android versions of QQ Browser. Our research shows that both versions of the application transmit personally identifiable data without encryption or with easily decrypted encryption, and do not adequately protect the software update process.
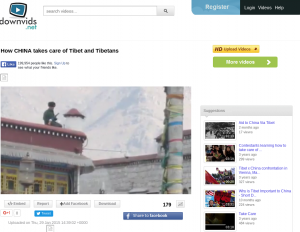
This report describes the latest iteration in a long-running espionage campaign against the Tibetan community. We describe how the attackers continuously adapt their campaigns to their targets, shifting tactics from document-based malware to conventional phishing
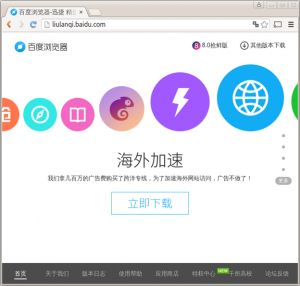
This report describes privacy and security issues with Baidu Browser, a web browser for the Windows and Android platforms. Our research shows that the application transmits personal user data to Baidu servers without encryption and with easily decryptable encryption, and is vulnerable to arbitrary code execution during software updates via man-in-the-middle attacks. Much of the data leakage is the result of a shared Baidu software development kit, which affects hundreds of additional applications.
This report describes major security and privacy issues in several leading wearable fitness tracking devices and accompanying mobile applications.
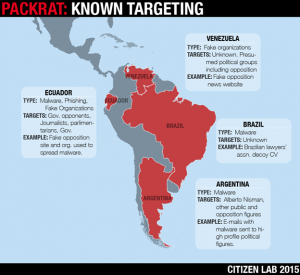
This report describes an extensive malware, phishing, and disinformation campaign active in several Latin American countries, including Ecuador, Argentina, Venezuela, and Brazil. The nature and geographic spread of the targets seems to point to a sponsor, or sponsors, with regional, political interests. The attackers, whom we have named Packrat, have shown a keen and systematic interest in the political opposition and the independent press in so-called ALBA countries (Bolivarian Alternative for the Americas), and their recently allied regimes.
A second audit of South Korea’s Smart Sheriff application reveals that there are numerous unresolved vulnerabilities that put minor children and parental users of the application at serious risk.
This report provides a detailed, mixed methods analysis of Information controls related to the Yemen armed conflict, with research commencing at the end of 2014 and continuing through October 20, 2015. The research confirms that Internet filtering products sold by the Canadian company Netsweeper have been installed on and are presently in operation in the state-owned and operated ISP YemenNet, the most utilized ISP in the country.
This report analyzes a campaign of targeted attacks against an NGO working on environmental issues in Southeast Asia. Our analysis reveals connections between these attacks, recent strategic web compromises against Burmese government websites, and previous campaigns targeting groups in the Tibetan community.
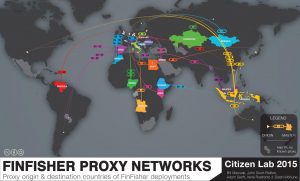
This post describes the results of Internet scanning we conducted to identify the users of FinFisher, a sophisticated and user-friendly spyware suite sold exclusively to governments.