Report
As the United Nations General Assembly begins its milestone 70th session, international digital security is high on the agenda. One starting point for discussion is likely to be the International Code of Conduct for Information Security (the “Code”). This analysis explores how the Code has developed over time, impetus behind the changes made, and the potential impact of the Code on international human rights law and its application. It is accompanied by an interactive comparison of the 2015 and 2011 versions of the Code.
This report describes the results of two independent security audits of Smart Sheriff, one by researchers who collaborated at the 2015 Citizen Lab Summer Institute (held at the Munk School of Global Affairs, University of Toronto), and the other by the auditing firm Cure53. The combined audits identified twenty-six security vulnerabilities in recent versions of Smart Sheriff (versions 1.7.5 and under). These vulnerabilities could be leveraged by a malicious actor to take control of nearly all Smart Sheriff accounts and disrupt service operations.
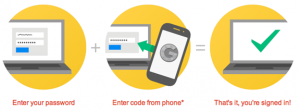
This report describes an elaborate phishing campaign using two-factor authentication against targets in Iran’s diaspora, and at least one Western activist.
This article, written by Postdoctoral Fellow Christopher Parsons and CIPPIC Staff lawyer Tamir Israel, analyzes how successive federal governments of Canada have actively sought to weaken the communications encryption available to Canadians. The article covers regulations imposed on mobile telecommunications providers, state authorities’ abilities to compel decryption keys from telecommunications providers writ large, and Canada’s signals intelligence agency’s deliberate propagation of flawed encryption protocols.
In this paper presented at USENIX FOCI 2015 we use reverse engineering to provide a view into how keyword censorship operates on four popular social video platforms in China: YY, 9158, Sina Show, and GuaGua. We also find keyword surveillance capabilities on YY. Our findings show inconsistencies in the implementation of censorship and the keyword lists used to trigger censorship events between the platforms we analyzed. We reveal a range of targeted content including criticism of the government and collective action. These results provide evidence that there is no monolithic set of rules that govern how information controls are implemented in China.
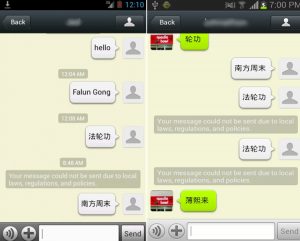
This research note outlines what we know about the use of Hacking Team’s Remote Control System (RCS) by South Korea’s National Intelligence Service (NIS). The note synthesizes information found in publicly leaked materials, as well as our own research.
This report is an analysis of the types of content removed by WeChat on its public accounts (also known as “official accounts”) blogging platform.
This post analyzes targeted malware attacks against groups in the Tibetan diaspora and Hong Kong that leverage the CVE-2014-4114 vulnerability
The report, authored by Postdoctoral Fellow Christopher Parsons, examines how contemporary telecommunications surveillance is governed in Canada. He concludes that serious failures in transparency and accountability indicate that corporations are failing to manage Canadians’ personal information responsibly and that government irresponsibility surrounding accountability strains its credibility and aggravates citizens’ cynicism about the political process.
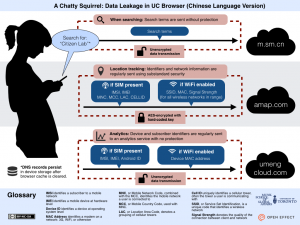
UC Browser is the most popular mobile web browser in China and India, boasting over 500 million users. This report provides a detailed analysis of how UC Browser manages and transmits user data, particularly private data, during its operation. Our research was prompted by revelations in a document leaked by Edward Snowden on which the Canadian Broadcasting Corporation (CBC) was preparing a story.