Introduction
This post analyzes targeted malware attacks against groups in the Tibetan diaspora and pro-democracy groups in Hong Kong. All of these attacks leveraged CVE-2014-4114 and were delivered via malicious Microsoft PowerPoint Slideshow files (*.pps). These attacks are highly targeted, appear to re-purpose legitimate content in decoy documents, and had very low antivirus (AV) detection rates at the time they were deployed.
The attacks against Tibetan groups shows a change in tactics from previous campaigns. Over the past four years the majority of attacks we have seen against Tibetan groups use CVE-2010-3333 or CVE-2012-0158. The use of CVE-2014-4114 marks the first time we have observed a change from this pattern in the last two years.
One attack sent to Tibetan groups used a link to a file on Google Drive to deliver the malware. Groups in the Tibetan community have promoted awareness campaigns around e-mail attachments, which have been the most common attack vector for the community. This campaign, “Detach from Attachments,” urges users to avoid sending or opening email attachments, and to use cloud-based storage to send files like Google Drive as an alternative. The use of Google Drive to send malware may be evidence of attackers adapting to the behavioral countermeasures promoted by the campaign.
In addition to the use of the same CVE, some of the attacks targeting Tibetan rights groups and Hong Kong groups have overlap in malware family (PlugX) and Command and Control (C2) domains. The similarities between these attacks suggests that either they are being conducted by the same threat actor or threat actors targeting these groups are sharing tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs).
Targeting and Social Engineering
We observed a total of five malware campaigns that used CVE-2014-4114 and a range of social engineering tactics to persuade recipients to either open an attachment, or visit a URL and download a malicious file.
In all of these attacks, if a recipient double clicks on the .pps file, they are shown decoy content. Examination of the exif metadata of the files indicates that the attackers are likely repurposing material from legitimate presentations.
PPT files (the more commonly used PowerPoint file extension) are automatically opened in edit mode, whereas .pps files are automatically opened in slideshow mode. For the CVE-2014-4114 exploit to work, the Powerpoint Slideshow needs to be played. Sending .pps files that automatically run a PowerPoint Slideshow is likely an attempt by the attackers to increase the infection rate.
Tibetan Attacks
Over April and May 2015 we observed 3 attack campaigns targeting a number of Tibetan organizations. The sophistication of the social engineering varied between attacks, but all attacks appeared to use re-purposed legitimate content.
Tibet Attack 1: April 2015
The first attack we observed was sent to multiple Tibetan groups over the course of April 2015. The email text is taken from a website related to an advocacy campaign and report by the International Tibet Network (ITN), a prominent Tibetan rights group. The email signature includes the real office address of ITN. However, the sender’s email address ([email protected]) is not a legitimate address related to the group. Attached to the email was a .pps file that repurposes slides from a presentation related to the same report and advocacy campaign referenced in the email message.
Tibet Attack 2: April 28, 2015
The second attack was sent out on April 28 2015 to multiple Tibetan organizations. The email message references a recent visit between Archbishop Desmond Tutu and His Holiness the Dalai Lama (HHDL). The .pps attachment also referenced the event and appears to be repurposed from legitimate material.
Tibet Attack 3: May 6 2015
The third attack was sent to Tibetan groups on May 6 2015 and contained a simpler message than previous attacks that urges the recipient to download a file from Google Drive, appears to repurpose legitimate content.
Dear Sir/Madam,
I have shared the Biography of H.H. THE 14TH DALAI LAMA via Google Drive.
Kindly download it.
PowerPoint Slideshow files do not display properly on Google Drive, and therefore a recipient may be tempted to download and open the file on their computer. The use of Google Docs is potentially evidence of attackers changing tactics in reaction to the Detach from Attachments campaign.
Hong Kong Attack Campaigns
We analyzed two attacks sent over the course of March 2015 that targeted individuals associated with human rights groups and pro-democratic political parties in Hong Kong.
Hong Kong Attack 1: March 6, 2015
The first attack was sent on March 6 2015. The email signature was made to appear to come from an assistant of Dr. Margaret Ng who is a Barrister and a former member of the Legislative Council in Hong Kong. The .pps attachment used a decoy document that appears to repurpose slides from an actual presentation Dr. Ng gave to Columbia Law School in February 2015.
Hong Kong Attack 2: March 31, 2015
The second attack was sent on March 31 2015, and contained a message related to the Occupy Central protests. The .pps file attachment was also related to Occupy Central and appears to repurpose legitimate content.
Infection
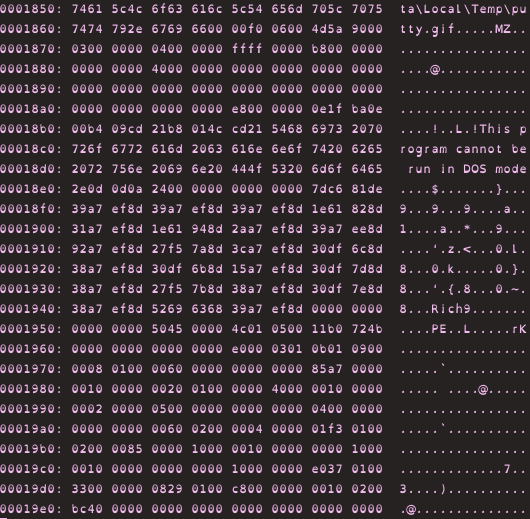
Despite the variety of targets and delivery approaches, the malware shares a common infection process. When the PowerPoint Slideshow is played, the malware leverages CVE-2014-4114, a vulnerability in the OLE Package Manager to infect the target machine. Computers using Windows Vista and above are susceptible to this attack. In addition to the decoy document, the malicious slideshow contains two embedded OLE objects: a .inf file and a malicious executable with a .gif extension that are dropped to the temp folder.
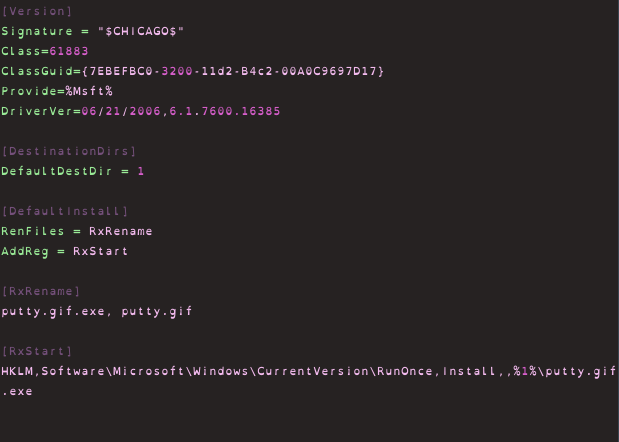
The .inf file is used to copy the executable and then run it.
The CVE-2014-4114 vulnerability has been described by Rapid7 and was previously linked to the “Sandworm” Russian threat actor. In these previously reported attacks, the .inf and .gif files are copied from a remote smb share to the victim’s computer. In the attacks we describe here the payload is embedded in the OLE objects, similar to cases described by TrendMicro.
Since CVE-2014-4114 is a vulnerability in the OLE package manager it makes it possible for attackers to create a PowerPoint presentation in which the OLE package manager loads a fake .gif file (that is actually a malicious executable), and then a malicious .inf file that runs the executable.
If a user double clicks on the malicious attachment, the decoy file opens without crashing the program or producing any other obvious signs that something is wrong with the file. This behaviour contrasts with how other common CVEs used to target groups in the Tibetan community (e.g, CVE-2012-0158, CVE-2010-3333) behave, which typically cause the vulnerable program to crash before opening a decoy document.
The exploit used in these attacks does not contain shell code, which makes it harder for AV heuristics to detect it. Of the samples we analyzed that have been uploaded to VirusTotal, two currently have 0 detections out of 57 AV engines (see Table 1).
Table 1: AV Detection Rates
| Sample MD5 | AV Detection Rate (Orignal Submission) | AV Detection Rate (Current) |
|---|---|---|
| 18bb1ce405e4abac4b0fc63054beac6c | Date / Time: 2015-04-30 13:44:39 Detection rate: 0/56 |
Date / Time: 2015-06-04 11:53:17 Detection rate: 0/57 |
| 8a18a13910838d08e38db80a08e15bd5 | Date / Time: 2015-03-06 02:30:16 Detection rate: 0/57 |
Date / Time: 2015-06-05 18:36:01 Detection rate: 0/57 |
| 2a544922d3ece4351c1af4ca63c24550 | Date / Time: 2015-05-06 09:28:05 Detection rate 8/57 |
Date / Time: 2015-06-05 18:38:17 20/57 Detection rate: 20/57 |
PlugX Attacks
Three of the sampled we analyzed used the PlugX malware family. PlugX is a well-known malware family that researchers have observed being used in targeted attacks against NGOs, government institutions, and private companies. A Trend Micro report on PlugX, describes a long-standing campaign that previously used Poison Ivy, another malware family. Jaime Blasco at AlienVault claims to have tracked down the author of PlugX, who is allegedly based at a Chinese security company.
In these three samples, the embedded executable in OLE is a self extracting RAR containing the three components of PlugX: a signed legitimate executable, a malicious DLL, and a binary file containing the main payload.
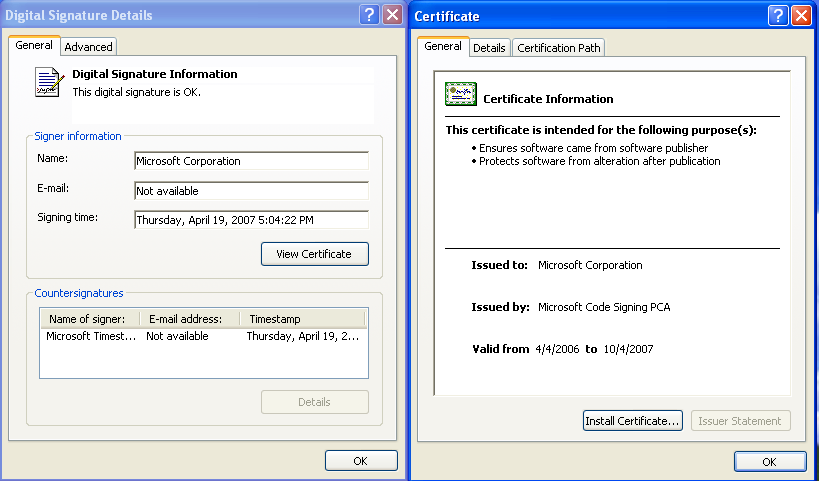
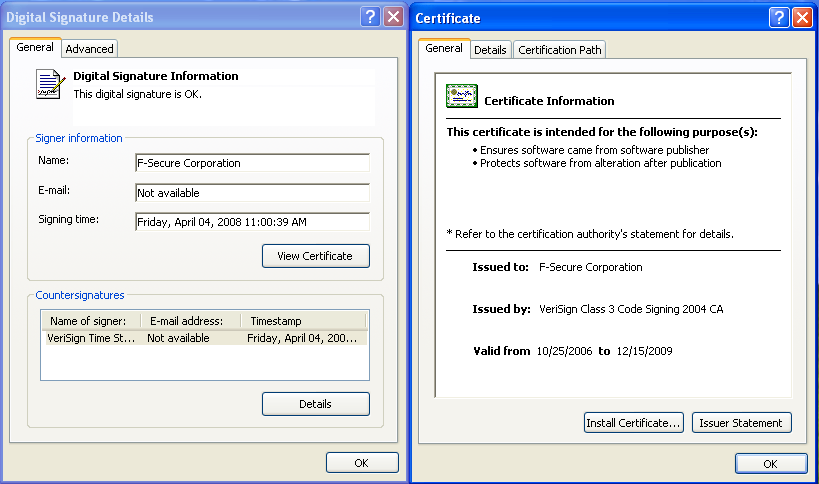
Using a technique known as DLL sideloading, the legitimate executable runs the malicious DLL. This malicious code then decrypts and decompresses the binary file in memory which contains the main functionality. Since the malicious code is being run by a signed, legitimate executable, and the payload never exists unencrypted on disk, it is more difficult for AV to detect PlugX.
For two of the three Plug X samples the the malware leverages expired certificates from legitimate vendors: one executable signed by Microsoft and one by F-Secure.
Connections to other Malware Families and Campaigns
While three attacks used PlugX malware, two other attacks did not. One of these attacks targeted Tibetan groups, the second targeted Hong Kong-based groups.
The non-PlugX attack against Tibetan groups communicates with free1999.jkub.com, a C2 that we have previously observed in multiple campaigns using the Surtr malware family and targeting Tibetan groups. The Valkyrie-X Security Research Group has also observed this C2 used in attacks against Hong Kong-based groups.
The non-PlugX attack against Hong Kong-based groups used a malware family that Symantec calls Wofeksad and connects to the C2 eset-windows.findhere.org. We have observed the Wofeskad malware family in another attack against a large International NGO that works on multiple countries and issues. However, that attack used CVE-2012-0158 and communicated with a different C2.
Details of the samples analyzed in this report are outlined in Table 2.
Table 2: Sample Details
| Sample MD5 | Delivery Mechanism | Targeted Group | Malware Family | Command and Control |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8a18a13910838d08e38db80a08e15bd5 | Email Attachment | Hong Kong | Wofeksad | eset-windows.findhere.org |
| 705147c509206151c22515ef568bac51 | Email Attachment | Hong Kong | PlugX (Sideload F-Secure) | dnsupdate.dynamic-dns.net |
| 18bb1ce405e4abac4b0fc63054beac6c | Email Attachment | Tibetan | PlugX (Sideload F-Secure) | dnsupdate.dynamic-dns.net |
| 2a544922d3ece4351c1af4ca63c24550 | Google Drive Link | Tibetan | PlugX (Sideload Microsoft Office 2003 component) | good.wha.la |
| d7832e76ee2c5c48ae428e57599b589e | Email Attachment | Tibetan | Not identified | free1999.jkub.com |
Conclusion
The re-purposed content, low AV detection rate, and the lack of any obvious signs to a user that the files are malicious (such as a program crash) make these attacks concerning. In the case of the Tibetan attacks, the use of CVE-2014-4114 shows a shift in tactics and a possible move away from CVE-2012-0158, which is the most commonly used CVE we have seen in attacks against the community. In addition, the use of Google Drive further suggests a potential change in tactics, possibly in response to behavioral countermeasures developed by Tibetan civil society.
The overlap in attacks against Tibet and Hong Kong groups also raises questions for future work. Are the attacks being conducted by the same threat actor, or is there sharing of TTPs between actors targeting these groups? Further analysis of attacks against these communities is needed to probe these questions.
Acknowledgements
Special thanks to Valkyrie-X Security Research Group.
The Citizen Lab’s research on Targeted Threats against Civil Society is supported by the John D. and Catherine T. MacArthur Foundation.
Indicators of Compromise
Tibet Attack 1
Attachment
File Name: Xi Jinping's Tibet Challenge.pps
MD5: 18bb1ce405e4abac4b0fc63054beac6c
Drops
File name: fsavstrt.exe
MD5: 9459478ab9a9b996de683789f77b185c
File name: FSMA32.dll
MD5: 8432c77b12343d59d991b0d0e0c12f7d
File name: FSMA32.dllfox
MD5: db5a9c790e909629aaf7079b6996861f
Command and Control:
dnsupdate.dynamic-dns.net
Tibet Attack 2
Attachment
File name: Desmond Tutu.pps
MD5: d7832e76ee2c5c48ae428e57599b589e
Drops
File name: putty.gif.exe
MD5: a990071b60046863c98bcf462fede77a
Command and Control:
free1999.jkub.com
Tibet Attack 3
Attachment
File name: H.H. THE 14TH DALAI LAMA.pps
MD5: 2a544922d3ece4351c1af4ca63c24550
Drops
File name: SX.exe
MD5: 5730866b34ef589bd398c9a9b6d7e307
File name: SXLOC.dll
MD5: d839691657ca814be13d5c9c6511d6b2
File name: SXLOC.zap
MD5: 03c900a1b115e759b32e4172dec52aa2
Command and Control:
good.wha.la
Hong Kong Attack 1
Attachment
Name: 「佔領中環」引發爭議的背後.pps
MD5: 705147c509206151c22515ef568bac51
Drops
File name: fsavstrt.exe
MD5: 9459478ab9a9b996de683789f77b185c
File name: FSMA32.dll
MD5: 8432c77b12343d59d991b0d0e0c12f7d
File name: FSMA32.dllfox
MD5: db5a9c790e909629aaf7079b6996861f
Command and Control:
dnsupdate.dynamic-dns.net
Hong Kong Attack 2
Attachment
File name: Speech and Media Freedom - New Lessons of the Umbrella Revolution.pps
MD5: 8a18a13910838d08e38db80a08e15bd5
Drops
File name: test.gif.exe
MD5: f90c7f8f14d9b5c1898035002401a006
Command and Control:
58.64.139.251