Report
This report examines algorithmic technologies that are designed for use in criminal law enforcement systems, including a human rights and constitutional law analysis of the potential use of algorithmic policing technologies.
As a follow-up to our March 2020 report, we conducted daily tests on WeChat and collected 2,174 censored keywords between January to May 2020. This data provides a view into how narratives and messaging on the pandemic are controlled and molded on social media in China.
Amidst calls for reform in Togo, NSO Group’s spyware was used to target voices for change including a bishop, priest, and opposition politicians.
Over the course of our multi-year investigation, we found that Dark Basin likely conducted commercial espionage on behalf of their clients against opponents involved in high profile public events, criminal cases, financial transactions, news stories, and advocacy. This report highlights several clusters of targets.
WeChat communications conducted entirely among non-China-registered accounts are subject to pervasive content surveillance that was previously thought to be exclusively reserved for China-registered accounts.
This report examines the encryption that protects meetings in the popular Zoom teleconference app. We find that Zoom has “rolled their own” encryption scheme, which has significant weaknesses. In addition, we identify potential areas of concern in Zoom’s infrastructure, including observing the transmission of meeting encryption keys to China.
The analysis of YY and WeChat indicates broad censorship—blocking sensitive terms as well as general information and neutral references—potentially limiting the public’s ability to access information that may be essential to their health and safety.
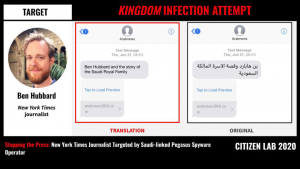
New York Times journalist Ben Hubbard was targeted with NSO Group’s Pegasus spyware via a June 2018 SMS message promising details about “Ben Hubbard and the story of the Saudi Royal Family.” The SMS contained a hyperlink to a website used by a Pegasus operator that we call KINGDOM. We have linked KINGDOM to Saudi Arabia. In 2018, KINGDOM also targeted Saudi dissidents including Omar Abdulaziz, Ghanem al-Masarir, and Yahya Assiri, as well as a staff member at Amnesty International.
This report presents results from a series of research projects that measured responses to personal data requests from telecommunication companies and Internet Service Providers across jurisdictions in Asia including Australia, Hong Kong, South Korea, Indonesia, and Malaysia. Overall, the projects found responses from telecoms were incomplete and in some cases did not follow what is required by law.
This campaign is the first documented case of one-click mobile exploits used to target Tibetan groups, and reflects an escalation in the sophistication of digital espionage threats targeting the community.