Netsweeper
The following is a statement from Citizen Lab Director, Ron Deibert, concerning a defamation suit recently filed, and then discontinued by Netsweeper against the University of Toronto and Ron Deibert.
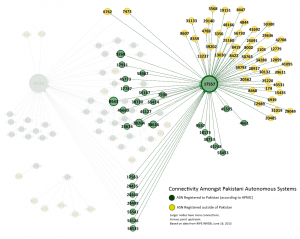
In June 2013, Citizen Lab released O Pakistan We Stand on Guard for Thee, a research report that reveals evidence that Internet filtering software developed by Canada-based company Netsweeper is deployed on networks operated by the Pakistan Telecommunication Company Limited (PTCL). PTCL is a formerly government-owned enterprise that currently serves as Pakistan’s largest ISP and the manager of its Internet Exchange Point. Previous research by the OpenNet Initiative indicated that Netsweeper is being used for national-level filtering in India and across countries in the Middle East and Gulf including Qatar, UAE, Yemen, India.
A new Citizen Lab report, entitled O Pakistan, We Stand on Guard for Thee: An Analysis of Canada-based Netsweeper’s Role in Pakistan’s Censorship Regime, has found that Canada-based Netsweeper filtering products have been installed in Pakistan, and are being used for filtering political and social web content.
In a Toronto Star article on the Guelph tech firm accused of making tools to censor Internet abroad, Citizen Lab Director Ron Deibert commented on the Canadian company’s controversial activities.
The Guelph Mercury newspaper reports that a Guelph-based tech firm called Netsweeper, which is known for making tools to control information abroad, is tightening communications at home. After giving several media interviews during its rapid rise in the burgeoning internet security sector, Netsweeper now not only refuses to speak to reporters, but also recently rejected a meeting request by Guelph MP Frank Valeriote.
In this article, CTV News reports on the role of Western companies in promoting censorship in the Middle East and North Africa. Specifically, it looks at Netsweeper Inc., a Canada-based developer of content filtering software, and its role in providing governments in Qatar, Yemen, and the United Arab Emirates with tools to filter online content.
Ron Deibert, director of the Citizen Lab, told CTV News that the recent controversy surrounding the Canadian company demonstrates that the Canadian federal government needs to take a clear position on content filtering, and within this, develop a clear foreign policy for cyberspace. For example, Deibert suggests that the Canadian government introduce legislation which makes it “illegal for Canadian companies to filter content in countries that violate the freedoms outlined in the United Nations Declaration of Human Rights.” In essence, “take a major international treaty of the 20th century, and apply it in a decidedly 21st century context.”
Deibert said that Canada should take on a leadership role on cyber policy “in international forums to spotlight and develop a kind of normative agreement that is consistent with the values we hold as a country.”
For the full article see here.
In light of the controversy around the use of Canadian-made software being used in the Middle East and North Africa, it is remarkable that the Ontario Centres of Excellence, the Information Technology Association of Canada, and the Canadian Department of Foreign Affairs would choose to honour an Internet Service Provider that pervasively filters access to information using Canadian made software.
See the OpenNet Initiative post here